
- #How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware how to
- #How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware update
- #How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware full
- #How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware code
#How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware update
I’ve been using WSL 2, which was officially released in the 2004 Windows update earlier this year.
#How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware full
WSL, or the Windows Subsystem for Linux, is an official component of Windows 10 that runs a full build of Linux right inside of Windows.

#How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware how to
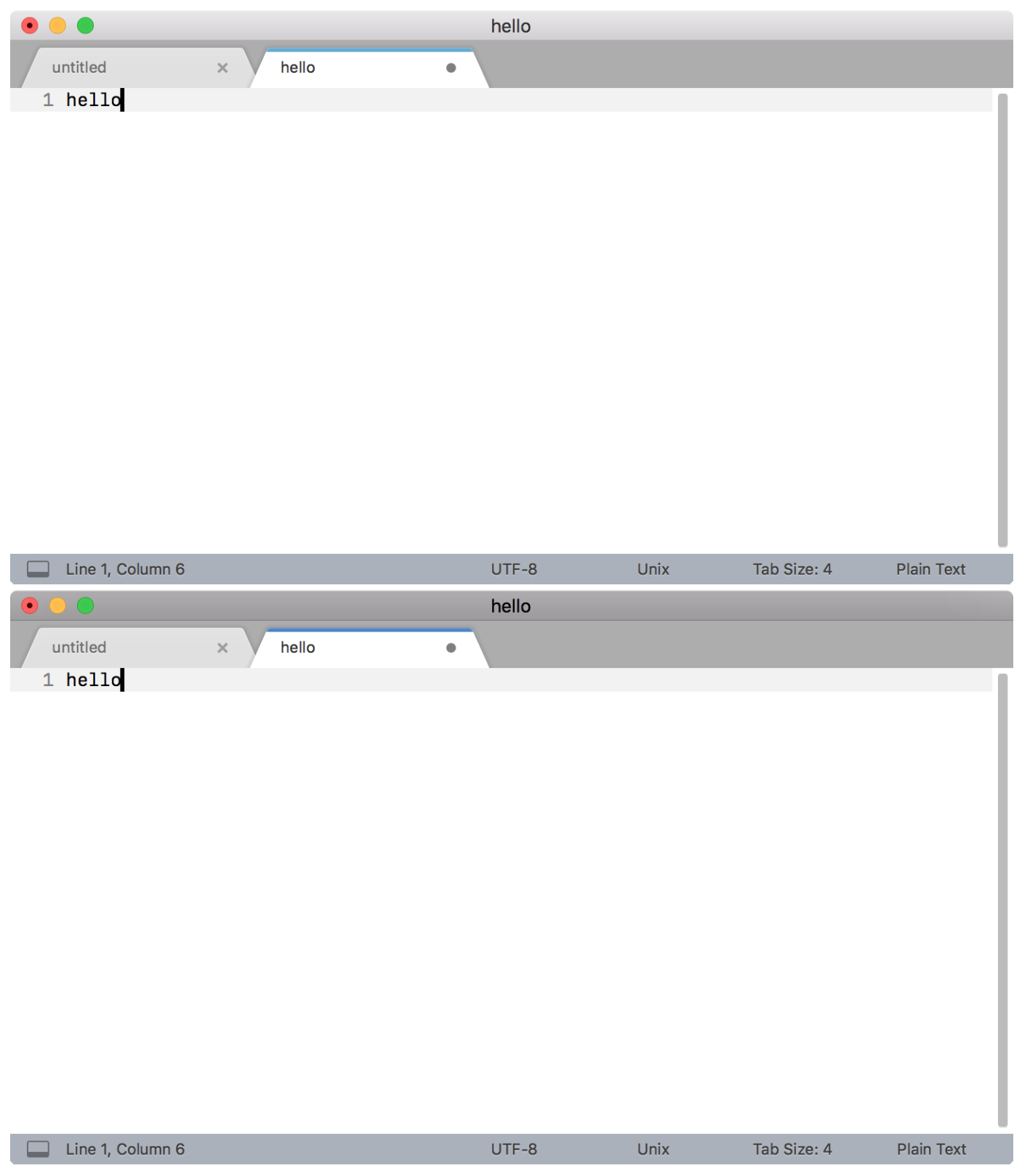
WSL provides an awesome tech-stack, so in this article I’ll show you how to set up your WSL2 environment for cross-platform development. I did most of my Beekeeper Studio development work in Ubuntu, running natively inside Windows, using the Windows Subsystem for Linux. It is like VSCode, but for SQL.īeekeeper Studio is built with Electron, a cross-platform desktop app development framework built on top of NodeJS and Chromium. If you have an improvement idea or run into a usability problem, please let us know by creating a YouTrack ticket.This year we released the first version of Beekeeper Studio, a cross-platform SQL editor and database manager. And of course, hearing back from you is really important. We will continue to enhance LightEdit in future IntelliJ IDEA releases so that you can do even more in a projectless mode. But in any case, you can change it before creating the project. The IDE will attempt to find a good location for the project root based on the presence of a Git repository, Gradle build files, and so on. If not, you will be prompted to choose a root directory where an IntelliJ IDEA project will be created. If the file is already under a project root, the project will be opened and an editor tab with the file will appear there. Go to File | Open File in Project…, or select Open File in Project… from the context menu, or choose the “ Open File in Project” intention by using Alt+Enter: Whenever you feel a few simple changes won’t be enough, and you need to use the capabilities of a full-blown IDE, you can switch to project mode right away. Expect more things to come in the future such as Git history, commits, and so on. Changes to the file are also shown in the editor, similar to usual project mode. If you open a file in the Git repository, you’ll see a widget showing the current Git branch. Git integrationīasic Git integration is available at the moment. Note: When IntelliJ IDEA is already running, the launcher doesn’t start another instance, but only makes the already running process create an editor window. There is one exception though: if the project to which the file belongs is already open, it will be opened in the project window as usual, that is, LightEdit mode will not activate. Then, click on a file, for example in Windows Explorer or Finder, to launch IntelliJ IDEA with the file opened in LightEdit mode: The same can be accomplished if a file is associated with the launcher script or executable in a system file manager. If you have an `idea` launcher script (Linux/MacOS) or `idea(64).exe` (Windows), you can open any file just by passing it as a parameter to the launcher: But if you just need to open a single file, make a few changes, and save, LightEdit is the quickest way to do it, and you don’t have to use a third-party editor either.
#How to download sublime text in ubuntu vmware code
The mode has certain limitations: it offers simpler code completion (or sometimes none at all), no code inspections, only basic code highlighting that doesn’t require sophisticated code analysis, and so on. In LightEdit mode, a file is opened in a separate editor window which may coexist with other (project) windows. As we talked about in an earlier blog post, LightEdit mode lets you use IntelliJ IDEA’s text editing features without creating or opening a dedicated project.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
